Introduction to PPF (Public Provident Fund)
The Public Provident Fund (PPF) is one of the most common and popular saving schemes, backed by the Government of India, making it a safe option for long-term investment. It is also one of the best ways to save tax. With disciplined investing, individuals can achieve significant wealth accumulation through PPF. For instance, by investing just Rs. 12500 per year for 25 years, one can accumulate a corpus of 1 crore rupees, showcasing the remarkable potential of this investment avenue. Therefore, individuals can opt for this investment scheme without any hesitation, knowing its potential to help achieve substantial financial goals.
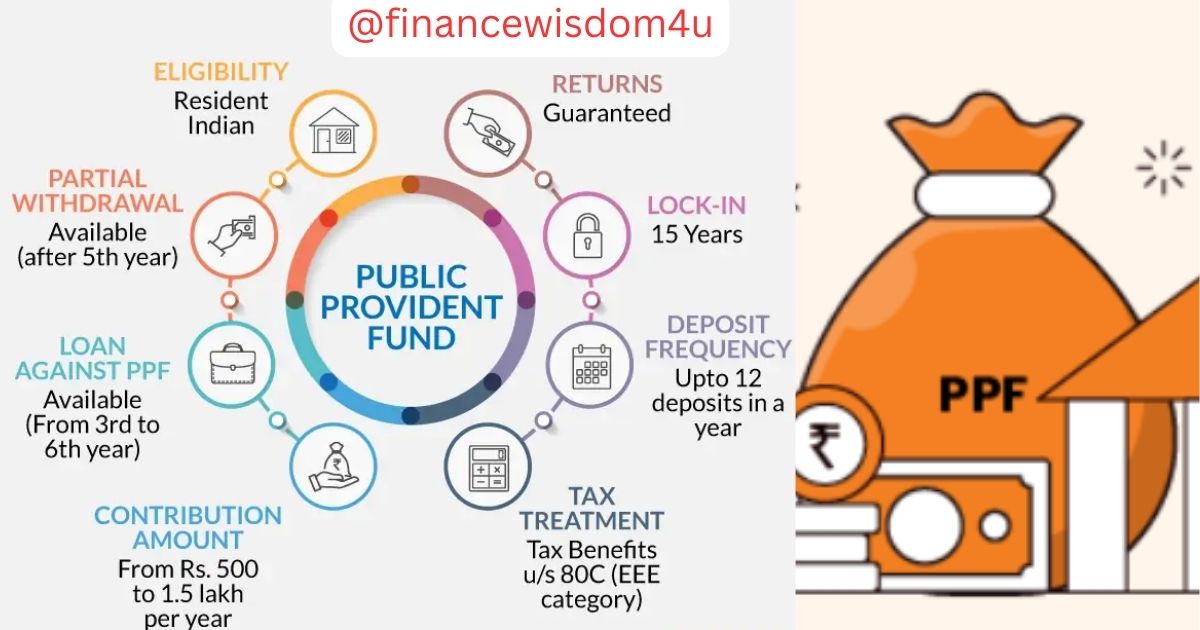
What is PPF?
The Public Provident Fund (PPF) scheme presents a long-term investment opportunity with appealing interest rates and returns on invested amounts. The interest earned and returns remain non-taxable under Income Tax regulations. To access these benefits, individuals must open a PPF account within the scheme, with yearly deposits eligible for Section 80C deductions. As per current regulations, individuals are limited to holding a single PPF account.
Importance of a PPF Account
A Public Provident Fund (PPF) scheme is well-suited for individuals who prefer low-risk investments. Being government-mandated, this scheme offers guaranteed returns, providing a safety net for the financial requirements of the general populace in India. Moreover, funds invested in a PPF account are not subject to market fluctuations.
Investors may also consider the Public Provident Fund scheme to add diversification to their financial and investment portfolios. During downturns in the business cycle, PPF accounts can deliver consistent annual returns, offering stability in investment performance.
Features of a PPF Account
The key characteristics of a public provident fund scheme can be listed as follows–
| Interest Rate of PPF | 7.1% per annum |
| Tax Benefit | Up to Rs.1.5 lakh under Section 80C |
| Risk Profile | Offers guaranteed, risk-free returns |
| Minimum Investment Amount | Rs. 500 per annum |
| Maximum Investment Amount | Rs 1.5 lakh per annum. |
| Tenure | 15 years |
PPF – Investment Tenure
A PPF account has a minimum lock-in period of 15 years for investments, during which funds cannot be completely withdrawn. An individual can choose to extend this tenure by 5 years after the PPF lock-in period is over if required.
PPF – Principal Amount
A minimum of ₹500 and a maximum of ₹1.5 lakhs can be deposited annually in a PPF account. Investments can be made in a lump sum or in a maximum of 12 installments.
Investments need to be made every year to keep the account active.
PPF – Tax Benefits
PPF offers EEE (Exempt-Exempt-Exempt) tax benefits.
Income tax exemptions apply to the principal amount invested in a PPF account. The entire investment amount is eligible for tax deduction under section 80C of the Income Tax Act of 1961. However, it’s important to note that the maximum principal amount that can be invested in one financial year cannot exceed Rs. 1.5 Lakh.
The total interest earned on PPF investments is also exempt from taxation.
Consequently, the entire amount withdrawn from a PPF account upon maturity is not taxable. This aspect makes the public provident fund scheme appealing to many investors in India.
PPF – Withdrawal
There are several conditions that investor must adhere to if they wish to withdraw funds from their PPF account.
A mandatory lock-in period of 15 years is imposed on the principal amount invested in these plans. However, in the case of emergencies related to specific end-uses, partial withdrawals are permitted. Nevertheless, this amount can only be withdrawn after the account has been active for 5 years. Additionally, up to 50% of the total balance can be withdrawn in a single transaction each financial year starting from the 4th year.
It’s important for investors to understand that funds invested in a PPF account cannot be liquidated before the maturity period is completed. Individuals seeking long-term, risk-free investment options with stable yields can easily opt for this government-backed instrument.
Withdrawal: A 15-year mandatory lock-in period is applied to the initial invested principal. In case of emergencies a person can withdraw partial amount after 5 years.
PPF – Premature Closures
In certain exceptional cases, PPF account can be closed before the maturity period (15 years). Such cases may include medical emergencies or higher education needs. However, there are specific conditions and penalties associated with premature closure.
Loan against PPF Investment
An individual can take a loan against the PPF from 3rd year to 6th year from the account opening year. The maximum loan amount you can take from your PPF account is capped at 25% of the balance in your account at the end of the second year preceding the year in which you apply for the loan.
For example, if you apply for a loan in the 4th financial year from the account opening, the loan amount will be based on the balance at the end of the 2nd financial year. The interest rate on the loan taken from a PPF account is usually lower than commercial loan interest rates.
Penalty
If the minimum contribution is not done for a financial year, then a penalty will be imposed. A penalty of Rs. 50 along with a minimum deposit of Rs.500 needs to be deposited to reactivate the account. If the contribution is not done for consecutive two financial years, then the account will be inactive and no interest will be earned.
PPF – Mode of Contributions
Deposits can be made in the form of cash, check, demand draft, or online transfer. Some banks and post offices may offer additional modes of deposit.
What is the interest rate on PPF?
The current PPF interest rate is 7.1% p.a. that is compounded annually.
The Finance Ministry set the interest rate every year, which is paid on 31st March. The interest is calculated on the lowest balance between the close of the fifth day and the last day of every month.
Further, use our PPF calculator to figure out the returns you can expect on investing a certain amount in a PPF account.
How to Become a Crorepati by Investing in PPF:
By investing Rs. 12,500 every month for 15 years, you will accumulate more than Rs. 40 lakh. However, if you extend this scheme twice for 5 years each, totaling 25 years, you can yield a total of Rs. 1.03 crore. Your total investment in this scenario will amount to Rs. 37.50 lakh. Notably, the interest earned will significantly increase. You will receive Rs. 65.58 lakh from interest alone.
It’s important to note that if you wish to extend the maturity period, you must inform your bank one year in advance. This strategic approach allows for substantial growth in your investment, leading to greater financial security and potential wealth accumulation in the long run.
How to Open a PPF Account?
Both offline and online procedures are available for individuals, provided they meet the requisite parameters outlined in the eligibility criteria. Activating a PPF account online can be accomplished by visiting the website of a chosen bank or post office.
The following documents must be provided at the time of activating a Public Provident Fund (PPF) account:
- KYC documents verifying the identity of the individual, such as Aadhaar, Voter ID, Driver’s License, etc.
- PAN card.
- Proof of residential address.
- Form for nominee declaration.
- Passport-sized photograph.
PPF Account Eligibility Criteria
- An individual must be a resident of Indian. Non-residents are not allowed to open a PPF account.
- Any individual, whether an adult or a minor, can open a PPF account. Parents or legal guardians can open accounts on behalf of minors.
Can you close PPF account before maturity?
A PPF account can be closed in special circumstances, such as life-threatening sickness faced by the account holder or dependents, paying for higher education, or a change in residential status, after 5 years from the date of opening.
Process to close a PPF account
As per the regulations governing PPF accounts, you can only fully withdraw your PPF account balance after the account completes its 15-year tenure. Upon the completion of this 15-year term, you gain access to the entire account balance, allowing you to withdraw it fully and close the account.
Before completing the full tenure of the account, withdrawing the entire account balance is not permitted under any circumstances. However, premature withdrawal of up to 50% of the account balance is allowed after 7 years, but only under special circumstances.
You have the option to close a PPF account after 15 years from the date of opening. The procedure to close a PPF account at the post office is outlined below:
Step 1: Fill out the necessary information in Form C and attach your PPF passbook.
Step 2: Submit the form to the relevant Post Office or bank branch where the account is held.
Step 3: Your application will be processed, and upon approval, the account will be closed. The payment will be credited to your savings account linked to the PPF account.
Process of transfer of a PPF account
You can transfer your PPF account to another branch of the bank/post office, switch from bank to post office, or switch from post office to a bank using the following procedure:
Step 1: Visit the bank or post office branch where your PPF account is currently held.
Step 2: Request the application form to transfer the PPF account and fill it out with the relevant details.
Step 3: The branch representative will process your application and forward it along with the certified copy of the account, nomination form, account opening application, specimen signature, and cheque/DD for the outstanding balance of the PPF account to the new branch.
Step 4: Once the new branch receives your application and supporting documents, you need to submit a new PPF account opening application along with the old PPF account’s passbook. You may also change the nominee at this point.
Step 5: After processing the application, your PPF account will be successfully transferred to the new branch.
Procedure to Withdraw PPF Money
If you wish to withdraw some or all of the funds from your PPF account, you can follow these steps:
Step 1: Complete the application form (Form C) with the required details.
Step 2: Submit the completed application to the bank branch where your PPF account is held.
What is Form C?
Section 1:
This section requires you to provide your PPF account number and the amount you wish to withdraw. Additionally, you must specify the number of years since the account was opened.
Section 2:
This section is for office use and includes details such as:
- The date of opening of the PPF account.
- The total balance in the PPF account.
- The date of the previous withdrawal request approval.
- The total available withdrawal amount in the account.
- The authorized withdrawal amount.
- The signature and date of the authorized person, usually the service manager.
Section 3:
This section requests information about the bank where the funds are to be credited directly or the bank in whose favor the cheque or demand draft is to be issued. You must also include a copy of the PPF passbook with this application.
Participating Banks Offering PPF account
Here is a list of participating banks where you can open a PPF account:
- Bank of Baroda
- HDFC Bank
- ICICI Bank
- Axis Bank
- Kotak Mahindra Bank
- State Bank of India
- Bank of India
- Union Bank of India
- Oriental Bank of Commerce
- IDBI Bank
- Punjab National Bank
- Central Bank of India
- Bank of Maharashtra
- Dena Bank
You can choose to open a PPF account at either the post office branch nearest to you or at one of these participating bank branches for your convenience.
How to activate an inactive PPF account?
To activate an inactive PPF account, follow these steps:
Step 1: Write a letter to the bank or post office branch requesting reactivation of the account.
Step 2: Pay the minimum amount of Rs.500 for each year without contributions, along with a penalty of Rs.50 for each inactive year.
Step 3: Submit the required payment and letter to the bank or post office.
Step 4: The bank or post office will process your request and reactivate the account accordingly.
PPF vs Mutual Funds
The Public Provident Fund (PPF) is a government-provided savings scheme that offers guaranteed returns. However, there are alternative investment options, such as mutual funds, which also offer tax-saving benefits. Mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool funds from multiple investors and invest them in various assets, including stocks and bonds.
Compared to PPF, mutual funds have the potential to generate higher returns and offer greater liquidity. They are categorized based on asset class, including equity, debt, and hybrid funds. Notably, only Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS) among mutual funds qualify for tax savings under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act.
Mutual funds have a track record of delivering returns that often outperform the market, making them a popular choice among investors. Each category of mutual funds has its investment objective and associated risk level.
Which is a better option: PPF or FD?
Choosing between PPF and FD depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment preferences. Here’s a comparison to help you decide:
- Tenure: FDs offer flexible tenures, while PPF has a fixed tenure of 15 years. If you prefer a short-term investment, FDs may be suitable, whereas PPF provides a stable, long-term savings option.
- Taxation: PPF offers tax-free returns, making it more tax-efficient compared to FDs, which are subject to taxation, including TDS.
- Interest Rates: FD interest rates vary among banks and may fluctuate over time. Senior citizens may receive higher interest rates on their FDs. PPF interest rates are determined by the government and are typically competitive.
- Loan Options: PPF allows for loans against the account, with a maximum limit of 25% of the balance between the 3rd and 5th year. FDs also offer loan facilities, allowing borrowers to access up to 90% of their deposit amount, typically at a higher interest rate.
- Loan Types: FDs can serve as collateral for various types of loans, such as home loans or business loans, depending on the bank’s policies. PPF loans are typically limited to personal loans against the account balance.
Ultimately, the choice between PPF and FD depends on your specific financial objectives and risk appetite. If you prioritize tax efficiency, long-term savings, and stable returns, PPF may be the better option. However, if you prefer flexibility in tenure, higher liquidity, and potential for higher interest rates, FDs could be more suitable. It’s essential to assess your financial situation and consult with a financial advisor before making a decision.
Is LIC better than Public Provident Fund?
Comparing LIC (Life Insurance Corporation) with Public Provident Fund (PPF) involves understanding their different purposes and benefits:
- Purpose:
- LIC: LIC primarily offers life insurance coverage with investment options through various policies like endowment plans and ULIPs (Unit Linked Insurance Plans).
- PPF: PPF is a government-backed savings scheme designed for long-term wealth accumulation and retirement planning. It offers guaranteed returns and tax benefits.
- Coverage:
- LIC: Life insurance policies from LIC provide financial protection to dependents in case of the policyholder’s demise.
- PPF: PPF does not provide life insurance coverage. It focuses solely on savings and investment.
- Returns:
- LIC: Returns from LIC policies may vary based on the type of policy chosen and market performance for investment-linked plans.
- PPF: PPF offers fixed, tax-free returns determined by the government. The interest rate is subject to change but is generally competitive.
- Tax Benefits:
- LIC: Premiums paid towards LIC policies qualify for tax deductions under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. Maturity proceeds may also be tax-free under certain conditions.
- PPF: Investments in PPF qualify for tax deductions under Section 80C, and the interest earned is tax-free.
- Flexibility:
- LIC: LIC policies often come with flexible premium payment options, coverage terms, and investment choices.
- PPF: PPF has a fixed tenure of 15 years with limited withdrawal options until maturity. However, it offers stability and security in returns.
- Cost and Complexity:
- LIC: Some LIC policies may have higher premiums and complex features, especially investment-linked plans like ULIPs.
- PPF: PPF is straightforward with no associated premiums or charges apart from penalties for non-maintenance or early withdrawals.
Ultimately, the choice between LIC and PPF depends on individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and insurance needs. While LIC offers life insurance coverage with investment options, PPF focuses on tax-efficient savings and stable returns. It’s advisable to assess your requirements and consult with a financial advisor before making a decision.
Limitations of Public Provident Fund (PPF)
It’s essential to carefully consider these limitation and assess your financial goals and circumstances before investing in a PPF account.
- Lock-in Period: PPF has a lock-in period of 15 years, longer than other tax-saving investments like Equity Linked Saving Scheme (ELSS) with a lock-in period of three years. This extended lock-in period may pose challenges during emergencies or when funds are needed. Premature withdrawals are allowed in PPF, but with restrictions and regulations on timing and amount.
- Moderate Interest Rate: The interest rate offered on PPF accounts is relatively moderate, especially considering its long-term nature. In contrast, ELSS has the potential to provide higher returns.
- No Joint Holding: PPF accounts cannot be held jointly, limiting options for joint ownership with family members.
- Investment Limit: The maximum annual investment limit in a PPF account is ₹1.5 lakh. However, other tax-saving instruments like ELSS funds, NPS, or FDs do not have such restrictions, although the maximum tax benefit remains capped at ₹1.5 lakh under Section 80C.
- NRI Restrictions: NRIs cannot open new PPF accounts. While NRIs with existing PPF accounts can continue making deposits, they cannot open new ones.
Conclusion
- Stability and Security: PPF offers stability and security as it is a government-backed savings scheme. This assurance makes it an attractive option for conservative investors who prioritize capital preservation.
- Tax Benefits: PPF provides tax benefits under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act, allowing investors to save on taxes while building long-term wealth. The tax-free nature of both the principal amount and interest earned enhances the overall returns.
- Discipline in Savings: The mandatory lock-in period of 15 years encourages disciplined savings habits, promoting long-term financial planning and wealth accumulation.
- Flexibility in Contributions: PPF allows flexible contributions, enabling investors to invest as per their financial capabilities, with a minimum deposit requirement of just ₹500 per year.
- Loan Facility: PPF offers a loan facility against the account balance, providing liquidity in times of need without disturbing the long-term savings objective.
- Retirement Planning: PPF can serve as an effective tool for retirement planning, offering a stable source of income post-retirement with tax-free withdrawals.
In conclusion, if you prioritize low-risk investments, value security, seek tax benefits, and aim for disciplined long-term savings, PPF emerges as a suitable choice. Its stability, tax advantages, flexibility, and retirement planning benefits make it an attractive avenue for conservative investors looking to build wealth steadily over time.
Learn with FinanceWisdom4U for more insights into India’s saving schemes and other investment options.
