Introduction
The Senior Secured Bond is a significant type of bond within the realm of investments and finance. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into various aspects of Senior Secured Bonds, shedding light on their features, advantages, and potential considerations for investors.Let’s understand senior secured bonds.
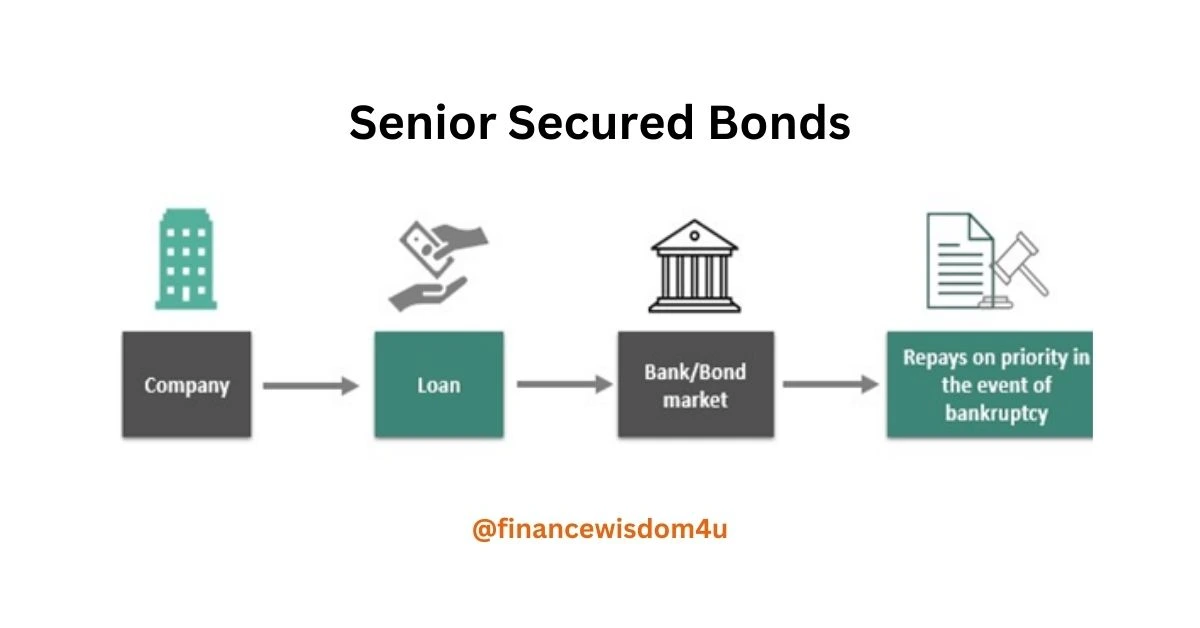
What is a Senior Secured Bond?
A Senior Secured Bond is a type of bond backed by collateral, providing a layer of security for bondholders. Senior Secured Bonds are prioritized over other debts in the case of liquidation, offering a reduced level of risk.
- Senior Secured Bonds have priority rights to receive payments over subordinated bonds and loans, unsecured bonds, and equity investors in the event of default by the issuer.
- Senior Secured Bonds are backed by collateral such as receivables, property, etc., which can be used to recover money in case of default by the issuer.
- Senior Secured Bonds are among the investment options available for investors seeking to diversify their portfolio while minimizing risk.
Importance of Senior Secured Bonds
Senior Secured Bonds play a crucial role in investment portfolios due to their relatively lower risk compared to other bond types. Investors often turn to these bonds for a secure and stable source of income.
Secured bonds gain support from specific tangible assets owned by the bond issuer. If the bond issuer defaults on repayments, bond investors, facilitated by a trustee, can sell these tangible assets to recover their investments.
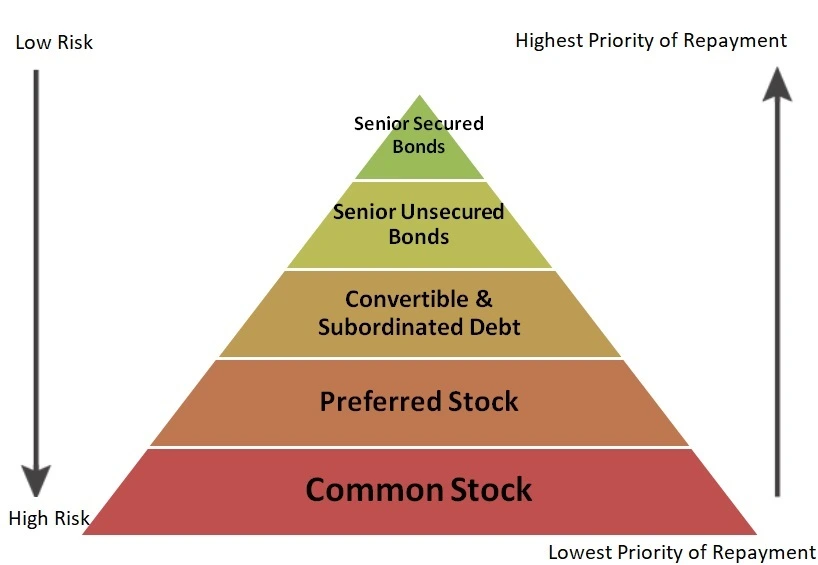
Every company structures its debt with a hierarchy that determines the order of debt repayment. Senior secured debt holds the highest seniority, ensuring that senior secured bondholders are the first to receive payments. This position makes senior secured bonds the safest form of debt for any company. In the event of the issuer’s bankruptcy, senior secured bondholders are prioritized for payment after the trustee sells off the issuer’s assets.
Junior and subordinate categories represent lower seniorities within the capital structure.
How do Senior Secured Bonds work?
Senior Secured Bonds are debt instruments through which a company raises funds from the public, providing investors with interest or coupon payments. Issued for a specified period, the bonds mature with the principal repaid to investors. These bonds hold a superior position compared to unsecured and subordinated bonds, granting priority to bondholders in payment during liquidation. The terms and conditions of interest and principal payments are predetermined by the issuer at the time of issuance, occurring on a schedule agreed upon, whether monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, or annually.
What are the features of Senior Secured Bonds
- Safety Features: Senior Secured Bonds stand out as a safer option among bonds, backed by collateral such as property, inventory, and receivables, offering investors a secure investment avenue.
- Priority in Liquidation: In the event of liquidation, senior secured bondholders take precedence over other investment holders, ensuring a higher priority in the repayment hierarchy.
- Credit Ratings: These bonds undergo assessment and rating by credit rating agencies, providing investors with valuable insights to make informed decisions based on the assigned ratings.
- Accessible Investment: Investors can enter the market with a minimum investment amount as low as Rs 1000. The specific terms of issuance dictate the range, typically falling between Rs 10,000 to Rs 1 Lakh.
- Collateral Backing: Assets such as property, inventory, and receivables secure senior secured bonds, establishing a safety net for investors and reinforcing their appeal as a secure investment option.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: Senior Secured Bonds come equipped with inherent risk mitigation strategies, enhancing their attractiveness as a secure and advantageous investment option.
Who issues Senior Secured Bonds?
Large corporations in India commonly issue these bonds as a means of raising funds from the market. Additionally, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) utilize senior secured bonds to secure borrowings from the public, providing an alternative avenue for funding in addition to traditional lenders like banks. NBFCs play a significant role as major issuers of bonds in the Indian debt capital market.
Similarly, in the United States, major corporations often issue these bonds as a method of sourcing funds from the market. Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) in the U.S. also utilize senior secured bonds to secure borrowings from the public, diversifying their funding sources beyond conventional lenders such as banks. NBFCs play a crucial role as significant issuers of bonds in the U.S. debt capital market.
Advantages of Senior Secured Bonds
- Stability: Explore the stability these bonds bring to an investment portfolio.
- Predictable Returns: Understand how the structure of these bonds provides predictability in returns.
- Collateral Support: Senior secured bonds stand out as a safer option due to their backing by collateral, providing an additional layer of security for investors.
- Stability in Returns: Unlike equity investments, senior secured bonds offer a safer investment avenue with fixed coupon payments on agreed-upon dates, ensuring a predictable and stable income stream.
- Regular Income: With a typical amortization structure, senior secured bonds provide investors with regular and periodic income. This characteristic makes them particularly attractive for individuals seeking a consistent source of income.
- Portfolio Diversification: Senior secured bonds offer a balanced approach for those looking to diversify their investment portfolio while maintaining a moderate level of risk. This makes them a suitable option for investors seeking stability and diversity in their financial holdings.
Disadvantages of Senior Secured Bonds
- Limited Liquidity: Senior secured bonds face challenges in terms of transferability and redeemability, resulting in low liquidity. This factor diminishes their attractiveness, especially during sudden financial needs when quick access to funds is crucial.
- Inherent Credit Risk: These bonds carry an inherent credit risk. If the issuer fails to maintain the quality of the hypothecated loan, there is a potential risk of default on timely payments. This credit risk adds a layer of uncertainty for investors.
- Moderate Returns: While senior secured bonds offer reduced risk compared to unsecured investment options, this safety comes at the cost of slightly lower returns. Investors should be aware that the trade-off for enhanced security is a potential decrease in overall returns.
Who should invest in Senior Secured Bonds ?
For investors seeking alternatives to traditional fixed-income instruments, senior secured bonds present an appealing option, offering higher interest rates than government bonds and fixed deposits while minimizing risk compared to equity investments and unsecured bonds. These bonds not only provide an opportunity for enhanced returns but also serve as a secure avenue for capital protection, ensuring investors can generate stable and regular income while prioritizing safety in their investment strategy.
Risks of investing in Senior Secured Bonds
The primary risk associated with investing in a senior secured bond emerges when the issuer defaults, and the collateral supporting the bond depreciates below market value. In such instances, investors might only recoup a fraction of their initial investments.
Additionally, senior secured bonds come with risks related to interest rates, coupon reinvestment, liquidity, and credit default. Holding a senior secured bond until maturity can mitigate interest rate and liquidity risks, providing a strategy to navigate these challenges effectively.
Senior Secured Bonds vs Government Bonds
Senior Secured Bonds and Government Bonds are two distinct types of fixed-income securities that investors can consider for their portfolios. Below is a comparison.
| Senior Secured Bonds | Government Bonds |
|---|---|
| 1. Backed by Collateral – Seniority in Repayment – Priority in Liquidation | 1. Backed by Government – Full Faith and Credit – No Collateral |
| 2. Higher Interest Rate and Moderate Risk | 2. Lower Interest Rate and Lower Default Risk |
| 3. Issuers : Corporate | 3. Issuers : Government |
| Aspect | Senior Secured Bonds | Government Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Backing | Backed by specific tangible assets owned by the issuer. | Backed by the full faith and credit of the issuing government. |
| Issuer Type | Typically issued by corporations seeking capital from the public. | Issued by national governments for various purposes, including funding public projects and managing national debt. |
| Risk Profile | Moderate risk; the level of risk depends on the creditworthiness of the issuer and the collateral. | Generally considered low-risk due to the backing of the government. |
| Interest Rates | Typically offer higher interest rates compared to government bonds. | Generally offer lower interest rates compared to other forms of debt due to lower default risk. |
| Default Risk | Risk of default exists, but collateral provides a layer of security for bondholders. | Considered low-risk, as governments are unlikely to default on their debt obligations. |
| Credit Rating Impact | May impact the issuer’s credit rating, with the impact depending on the seniority in the capital structure. | May have a direct impact on the government’s credit rating. |
| Liquidity | Liquidity may vary; may be less liquid compared to government bonds. | Generally more liquid, providing ease of buying and selling in the market. |
| Investor Base | Appeals to investors seeking a balance between risk and return. | Attracts a wide range of investors, including those seeking safety and stability. |
| Income Requirements | Potential for higher returns, making them attractive to income-seeking investors. | Provide stable and predictable returns, making them suitable for income-oriented investors. |
Considerations for Investors:
- Risk Tolerance: Investors with a higher risk tolerance may find senior secured bonds attractive for their potential higher returns.
- Safety Preference: Those prioritizing safety may lean towards government bonds due to the lower default risk.
- Income Requirements: Investors seeking regular income may evaluate the interest payment structure of both types of bonds.
Ultimately, the choice between Senior Secured Bonds and Government Bonds depends on an investor’s financial goals, risk appetite, and the current economic environment. Diversification across different asset classes is often a strategy to balance risk and return in a portfolio.
Covered Bond vs Senior Secured Bond
Covered Bonds and Senior Secured Bonds represent distinctive financial instruments with unique features and applications in the investment landscape. Understanding the differences between these two types of bonds is essential for investors seeking to diversify their portfolios and manage risk effectively. The following table provides a comprehensive comparison of Covered Bonds and Senior Secured Bonds, highlighting key aspects such as backing, risk profiles, investor bases, and more. This information aims to empower investors with valuable insights to make informed decisions aligned with their investment goals.
| Aspect | Covered Bonds | Senior Secured Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Backed By | Pools of high-quality, low-risk assets, often residential mortgages or public sector loans. | Specific tangible assets or collateral owned by the issuer, providing security for bondholders. |
| Issuer Type | Typically issued by financial institutions, often banks. | Issued by corporations seeking capital from the public. |
| Security | Dual recourse: Bondholders have a claim on both the assets in the cover pool and the issuer’s general assets. | Bondholders have a claim only on the specified collateral backing the bonds. |
| Risk Profile | Generally considered low-risk due to dual recourse and high-quality asset pools. | Moderate risk, with the level of risk dependent on the creditworthiness of the issuer and the collateral. |
| Credit Rating Impact | Covered bonds may have a limited impact on the issuer’s credit rating. | Senior secured bonds may impact the issuer’s credit rating based on their seniority in the capital structure. |
| Liquidity | Generally more liquid compared to senior secured bonds. | Liquidity may vary, and these bonds may be less liquid than covered bonds. |
| Investor Base | Attracts a wide range of investors, including those seeking a safe haven. | Appeals to investors seeking a balance between risk and return. |
| Regulation | Subject to specific regulations, often involving cover pool requirements and regulatory oversight. | Regulatory requirements may vary, and they may not have the same specific regulations as covered bonds. |
In summary, the table illustrates the nuances between Covered Bonds and Senior Secured Bonds, offering a detailed perspective on their characteristics, risks, and market presence. Covered Bonds, with their dual recourse structure and high-quality asset pools, often attract investors seeking a low-risk investment avenue. On the other hand, Senior Secured Bonds, backed by specific tangible assets, provide a balance between risk and return for those looking to diversify their investment portfolio.
Investors should carefully evaluate their risk tolerance, income requirements, and investment objectives when choosing between Covered Bonds and Senior Secured Bonds. Additionally, market conditions and regulatory landscapes may influence the attractiveness of these bonds, emphasizing the importance of staying informed and adapting investment strategies accordingly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Senior Secured Bonds emerge as a reliable and secure investment option in the financial markets. The unique combination of their prioritized position in the repayment hierarchy and the tangible backing of collateral establishes them as an appealing choice, particularly for investors who prioritize risk mitigation in their portfolios. Senior-Secured Bonds are a safe and stable way to invest your money. They’re like a reliable path that helps you balance and navigate through the ups and downs of the financial world. So, if you want a secure and smart investment, Senior-Secured Bonds are a good choice.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is a Senior Secured Bond Safe?
Senior secured bonds are a comparatively safer option for investing in bonds. In the event of default or liquidation, investors in senior secured debt will be prioritized over unsecured debt and equity.
2. How does Senior Secured Bond differ from other Bonds?
Senior Secured Bonds distinguish themselves through the assurance of collateral and priority repayment, setting them apart from other bond types that might lack such safeguards. It’s essential to delve into the detailed comparison section to grasp these distinctions thoroughly before finalizing any investment decisions in the realm of bonds.
3. What types of assets can be used as collateral for Senior Secured Bonds?
Various types of assets can be used as collateral for Senior Secured Bonds. Common examples include below
- Real Estate: Properties such as land, buildings, or other real estate assets can serve as collateral.
- Inventory: Tangible goods held by a company, especially in manufacturing or retail, can be used as collateral.
- Receivables: Future payments that a company expects to receive from its customers can be pledged as collateral.
- Equipment and Machinery: Physical assets like machinery, vehicles, or equipment owned by the company can be used to secure bonds.
- Financial Instruments: Marketable securities, such as stocks or bonds, may be used as collateral.
- Intellectual Property: Patents, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property assets can sometimes be utilized.
- Contracts: Certain contractual rights or agreements may be pledged as collateral.
The specific assets accepted as collateral can vary based on the terms of the bond issuance and the agreement between the issuer and bondholders. Investors should carefully review the offering documents and prospectus associated with Senior Secured Bonds to understand the nature of the collateral backing the bonds.
4. Are Senior Secured Bonds suitable for risk-averse investors?
Yes, Senior Secured Bonds are suitable for risk-averse investors due to their secured nature and priority in repayment during default or liquidation.
5. Can the priority of repayment change over time?
The priority of repayment for Senior Secured Bonds remains relatively stable over time, typically maintaining their secured status in the event of default or liquidation.
6. How do market conditions affect Senior Secured Bond performance?
Market conditions can impact Senior Secured Bond performance, influencing factors such as interest rates, credit spreads, and investor sentiment.
7. Are Senior Secured Bonds affected by interest rate changes?
Yes, Senior Secured Bonds can be influenced by interest rate changes, impacting their performance in the financial market.
8. How to buy Senior secured bonds in India?
Investors in India can buy senior secured bonds through their Demat accounts, either by subscribing to primary issuances (RBI retail Direct) or purchasing them in the secondary market. Additionally, there are online bond platforms where investors can register and buy these bonds. Through bondsindia , wint-wealth, golden-pi,etc platform investor can buy.
9. How do I buy senior secured bonds?
You can buy senior secured bonds through financial institutions, brokerage firms, or participate in bond issuances through stock exchanges, ensuring compliance with regulatory procedures and market conditions. Even if you have a demat account, you can subscribe to primary issuances, buy in the secondary market, or utilize online bond platforms for transactions.
10. What is an example of a Senior Secured Bonds
- Barings global senior secured bond fund
- 8.05 hdfc ltd 2029 bond senior secured
- Many more search in bondsindia , wint-wealth, golden-pi,etc platform in India
Learn more about such topics with FinanceWisdom4U and continue to learn and become financially independent.
